Related links
- The ATLAS website
This website is no longer maintained. Its content may be obsolete. Please visit http://home.cern for current CERN information.
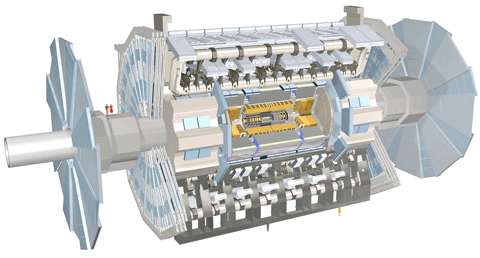
ATLAS is one of two general-purpose detectors at the LHC. It will investigate a wide range of physics, including the search for the Higgs boson, extra dimensions, and particles that could make up dark matter. ATLAS will record sets of measurements on the particles created in collisions - their paths, energies, and their identities.
This is accomplished in ATLAS through six different detecting subsystems that identify particles and measure their momentum and energy.
Another vital element of ATLAS is the huge magnet system that bends the paths of charged particles for momentum measurement.
The interactions in the ATLAS detectors will create an enormous dataflow. To digest these data, ATLAS needs a very advanced trigger and data acquisition system, and a large computing system.
More than 2900 scientists from 172 institutes in 37 countries work on the ATLAS experiment (December 2009).